You may think of wood as an unsophisticated and old-fashioned material. When looking back on wood’s use in technology your mind may immediately revert back to when airplanes and ships were made of wood. Wood technology goes back to when humans were crafting weapons, wheels, tools for cooking and nearly any technology of the past. Today wood products is making a great comeback just like its older times to start a new revolution for our future. New possible ways of using wood are evolving. When thinking about skyscrapers, tires, bottles, personal care products, medicines or even computer screens, start thinking wood. Interesting right? The reality is that as a renewable treasure, wood can help us substitute materials like steel, aluminum, plastic, and concrete which demand high and extensive energy to produce. Let’s jump right in and see how wood has an important role in our future.
"Plyscrapers": The New Wooden Skyscrapers!
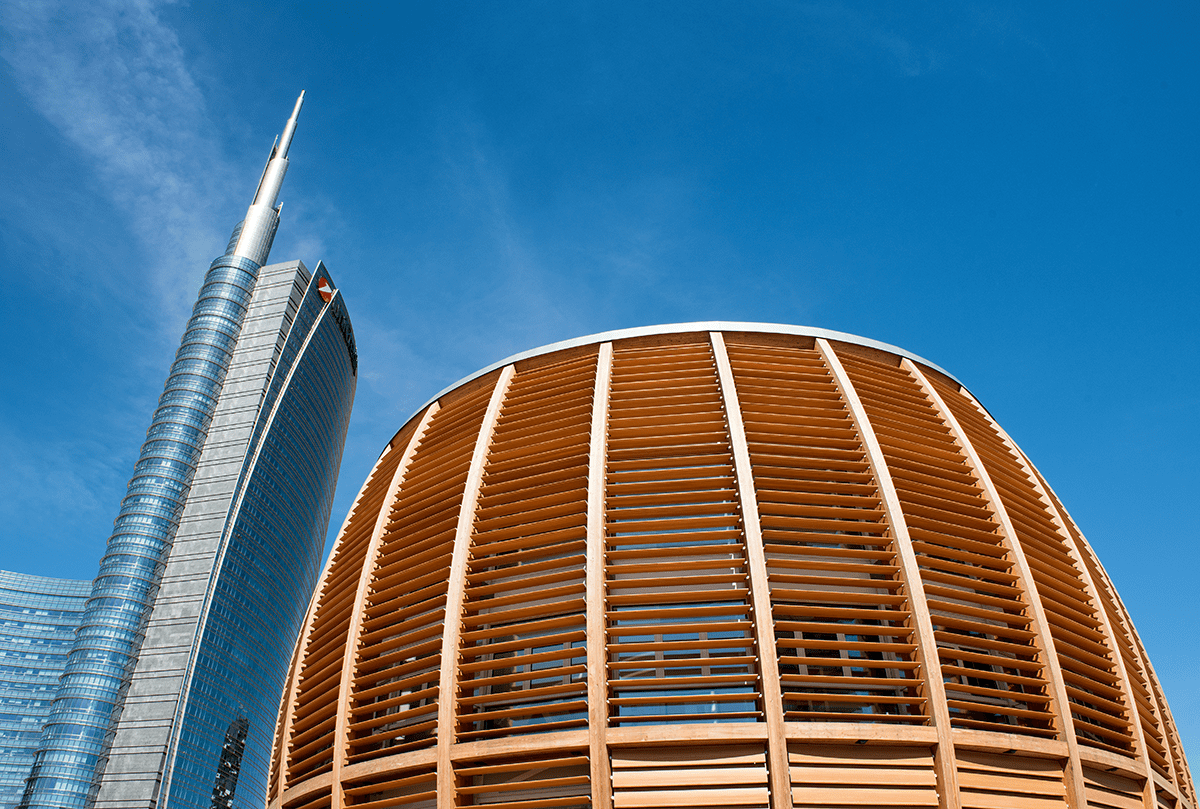
Building with wood is not new as it has been used as a building material for many years. However, now even tall wood buildings being called “plyscrapers” are spreading across the world and going towards replacing or at least competing with skyscrapers.
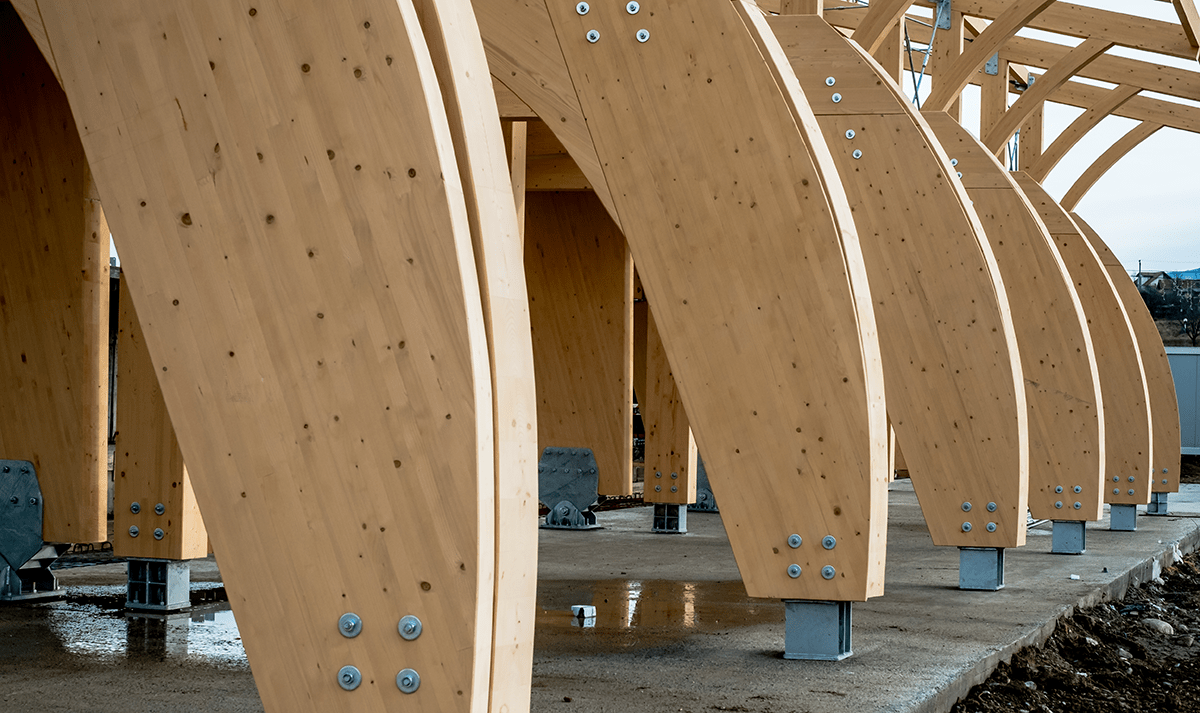
Okay, you may be thinking, wood is a flammable material that is also susceptible to rot, unlike steel and concrete. But a new material called cross-laminated timber (CLT) is making way for plyscrapers to take over!
CLT is a prefabricated, solid engineered wood panel that is made from multiple layers of kiln-dried timber boards crisscrossed and glued together with structural fire-resistant adhesives and pressed to form a firm, straight, rectangular panel(1) that can strongly resist against warping. The material is lightweight yet just as strong as structural steel and it is fast and easy to install, substantially accelerating the construction process and has a much lower carbon footprint than steel and concrete buildings greatly benefiting the environment(2). The required fire-resistance periods for multi-story buildings are measured between 30 and 120 minutes(3), CLT panels can achieve a 90-minute fire-resistance and unlike steel(4) it remains structurally stable when subjected to high temperatures(5).
Timber is known for its extreme durability especially with the right maintenance. Some ancient wooden buildings still exist regardless of environmental factors. Consider the Pagoda of Fogong Temple that was built without a single nail, screw, or bolt and has survived at least seven serious earthquakes(6). Incredible right? Well, unlike concrete and steel, timber is known for its flexibility so when the ground starts trembling wooden structures tend to sway without collapsing. Plyscrapers are currently taken into consideration across the globe. Norway is currently building an 18-story “plyscraper” and in Japan there are plans for a 350-meter tall tower in Tokyo(7)!
Wood Products In The Tech World
Can you imagine a brown stiff wooden board as a computer screen? It sounds ridiculous, but believe it or not “transparent wood is already possible”, Said Marc Pilahi from the European Forest Institute(8). This could be achieved by using wood-based nanocellulose. In fact, plant cells are formed from cellulose, and now microfibers of it can be extracted from wood using chemicals and pressure(9). Bendable mobile phones already exist and are constantly in development. Scientists in Singapore have come up with nano paper, which can conduct electricity and could be used in foldable computers(10). When this becomes a reality you won’t need a laptop bag anymore.
Stabilizers play a crucial role in the production of cosmetics. Microfibrillated cellulose that can be produced from sustainable forestry materials is a highly effective stabilizer that can be used in creams and beauty products (11). Have you ever imagined that wood could hold your face cream together? Wood’s potential continues to surprise us and is greatly climbing its way to make our future better.
Wooden Scaffolds and Medical Advances
When we break a bone it normally starts to get regenerated by stem cells which are produced by our own body. Not only are nutrients needed for these cells to get produced, but these cells also need a scaffold they can adhere to that can guide their growth into the bone(12). So here comes the role of nanocellulose in regrowing shattered bones. It is basically a solid enough jelly material that can take the shape of any object you attach it to (13). This nanocellulose scaffold would help to regenerate broken bones until the bones are set and then it breaks down into cells that can be penetrated by the body and used as energy(14).
In short, a lot of wood products and uses are emerging and are starting to make crucial developments towards processes that reduce fossil fuel use, boost human safety and lead to a healthier environment. What can you imagine they will make out of wood next?
(1) (2) David N. Bengston, “The Revolutionary Role Of Wood In Our Future”[Blog], USDA, Aug 03, 2021, https://www.usda.gov/media/
(3) “structural fire resistance requirements”, SteelConstruction.info, https://www.steelconstruction.
(4) (5) “Crosslam timber / CLT-Fire resistance and rating”, greenspec, https://www.greenspec.co.uk/
(7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) ” Eight things we’ve learned about the future of the wood”, BBC, https://www.bbc.co.uk/